Serverless Deployment of web application (PART 1)
SERVERLESS DEPLOYMENT OF WEB APPLICATION !!
What is Serverless?
Serverless computing allows developers to build applications without managing infrastructure. While servers exist, they are managed by cloud providers like AWS. This lets developers focus more on writing code rather than handling infrastructure.
Need for Serverless
Better Scalability: Automatically handles traffic spikes.
Auto Provisioning: No need to manually allocate resources.
Cost Optimization: Pay only for the resources used, not for idle servers.
Traditional vs. Serverless Deployment
In a traditional setup using EC2, we manage CPU, RAM, and storage. Even if the application receives low traffic, we must pay for the full server capacity. With serverless, resources are allocated dynamically based on demand, reducing costs.
This guide is divided into two parts:
Part 1: Setting up a DynamoDB table and AWS Lambda function.
Part 2: Creating an API to trigger the Lambda function and hosting a static web application using S3.
Now, let’s begin with Part 1, where we will create a DynamoDB table and configure Lambda.
Pre-requisites
1.AWS account
2.IAM role to allow Lambda to access DynamoDB
Part 1: Setting up a DynamoDB table and AWS Lambda function.
Now in the AWS console search for "AWS Lambda" in the search box and click on "Create a function" button
We have seen how "getStudent" function have been created , similarly create a a function with the name "insertStudent".
The code part of "insertStudent" function can be written in the code part . Then after deploying successfully then test the code.
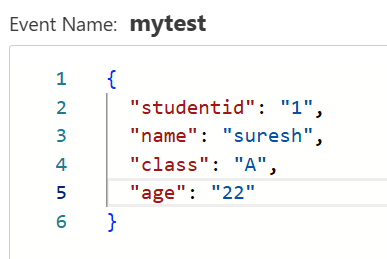
Pass the following test case with suitable arguments as shown
Now we can see that the arguments passed in the "insertStudent" has been reflected in the dynamoDB database table that we have created [dynamoDB]























Comments
Post a Comment